TROUBLESHOOTING
A/C PERFORMANCE TEST
An accurate diagnoses and determination of air conditioning system function and more importantly, malfunction, depend largely upon the ability of the technician to interpret gauge pressure reading. The importance of a refrigerant technicians’ manifold and gauge set is often compared to that of a doctor’s stethoscope. Your technician determines the quality of your A/C Performance Test.
Firstly, an improper gauge reading will relate to a specific a/c performance test problem. More than one problem may be associated with particular gauge reading, however. A system operating normally will have a low side gauge pressure reading that corresponds with the temperature of the liquid refrigerant as it becomes a vapor while removing heat from the air flowing over the evaporator coil surface. The high side gauge readings should correspond with the temperature of the vapor as it becomes a liquid while giving up its heat to the ambient air flowing through the condenser.
Secondly, any deviation from ambient dependent normal gauge readings, other than slight, indicates a malfunction. This malfunction, if within the system, may be caused by a faulty control device, a restriction or a defective component. It should be noted that improper mounting or location of components in a newly installed system may affect system performance. The vehicle engine may also affect system performance and will be noted as abnormal gauge readings.
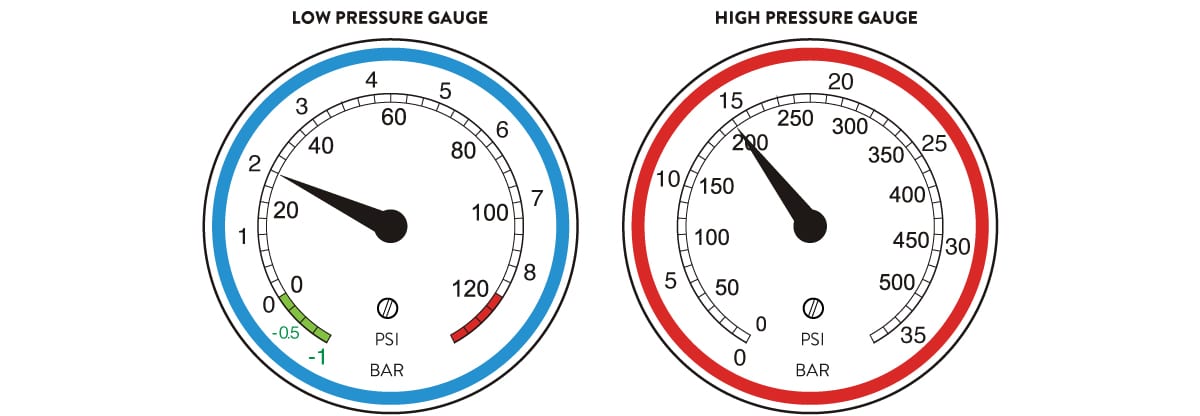
PRESSURE GAUGE PRE-CHECK
For your A/C Performance Test, always inspect pressure gauges to ensure the needles rest as zero on both low and high sides on atmospheric pressure. If the needle(s) do not rest on zero, remove the hoses, open both taps, detach the dial face and gently turn the adjustable screw until the needle(s) rest on zero. Reconnect hoses and close taps.
PRESSURE GAUGES READING IN NORMAL CONDITION
Gauges shows normal operation of A/C system. If the pressure readings to the ambient temperatures are different to these, then the system is probably defective. Note: Pressure gauge readings (low and high) depends on outside temperature.
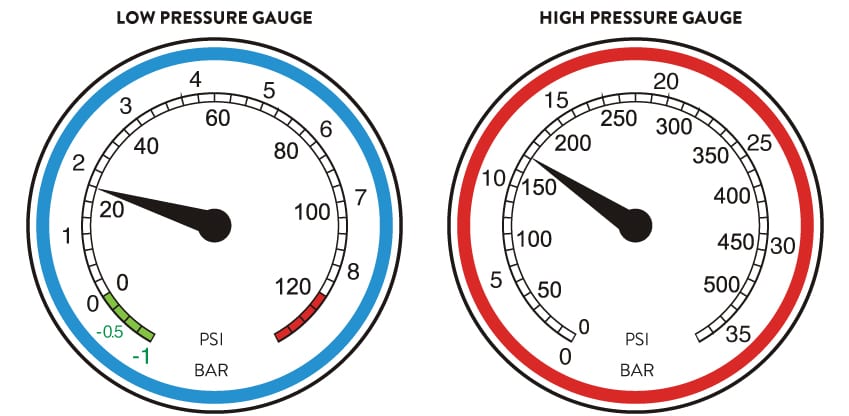
SUCTION PRESSURE VS. AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
Example: The outside temperature is 25 C. The suction pressure we have measured is pressure.

PRESSURE GAUGES READING
PROBABLE CAUSES

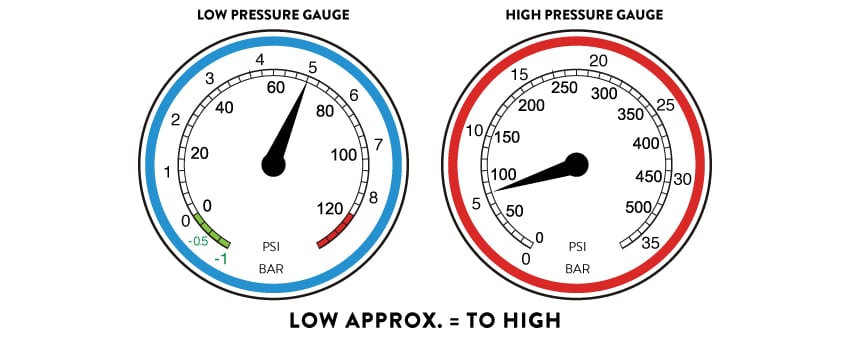
Pressure readings are normal, A/C system is not cooling.
-
• Warm air infiltrated into the evaporating unit or passenger compartment.
-
• Warm water infiltrated in the heater.
-
• Ice on evaporator core.

-
• Normal situation if ambient temperature is very low.
-
• Too little refrigerant quantity, 70-75% less. check for leaks.
-
• (V) Expansion valve stuck partially closed or blocked
-
• (V) Clogging in the H.P. or L.P. branch between filter and evaporator.
-
• Blockage in the H.P. branch between compressor and condenser-filter hose, but before the H.P. reading point.

-
• Normal situation if ambient temperature is very high.
-
• Excess refrigerant charge, 30-5% more.
-
• Condenser overheated.
-
• Air present in the A/C system.
-
• (V) Compressor displacement regulator valve defective.
-
• Blockage in the H.P. branch between compressor and condenser filter hose, but after the H.P. reading point.
-
• Compressor belt jumped. Probably caused by misalignment of the pulleys
-
• Electric clutch of the compressor not engaged.
-
• Compressor damaged.
-
• (V) Compressor displacement regulator valve defective.

-
• Suction and drainage hoses reversed on compressor.
-
• Electric clutch of the compressor not engaged.
-
• Expansion valve stuck open. If the compressor is “variable displacement type”, the low pressure has small but fast oscillations.
-
• (V) Compressor displacement regulator valve incorrectly set or defective
-
• Compressor damaged

-
• Filter saturated with moisture
-
• (V) Compressor displacement regulator valve stuck at maximum displacement.
-
• (F) Blockage in H.P. or L.P. branch between filter and evaporator.
